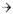 LIGHTBROWN APPLE MOTH LIGHTBROWN APPLE MOTH

Hand lens view: Mature LBAM caterpillars eat flowers and young bunches
Photo credit: DeAnn Glenn

Look for in leaves- Egg masses on the upper surface of fully expanded leaves
- Egg masses during the week before, and young caterpillars immediately after, a predicted egg hatch
- Egg masses and small caterpillars every 7-14 days from budburst, if there is no alert system for LBAM activity in your district
- Tiny, pale yellow caterpillars inside shoot tips, in leafrolls, at flowering or in young bunches, and on the underside of mature leaves
- Favours cool climates, lush growth and cool summers
- Females lay most of their eggs two or three times a season, during and just after peak flights.
- Freshly laid egg masses are green, become yellow and turn yellow-brown with a small black dot in the centre when ready to hatch.
- Eggs hatch within 7-21 days, depending on termperature - the warmer it is the quicker they develop.
- Caterpillars hide in webbing in leaf rolls or bunches. When disturbed, they wriggle backwards quickly and may hang by a thread.
- Tight-bunched varieties such as Chardonnay, Pinot Noir and Sauvignon Blanc are most susceptible to LBAM.
**Parasitised LBAM eggs turn black
**Egg hatch may occur over a number of weeks
**Empty egg masses may indicate a recent hatch, but they can stay on leaves for some time
**Monitor to find newly hatched caterpillars because large caterpillars are difficult to control
**Monitor after spraying to look for surviving caterpillars inside shoot tips and on the underside of the first four or five leaves (on five shoots per panel)
|
|
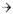 OTHER LIGHTBROWN APPLE MOTH IMAGES OTHER LIGHTBROWN APPLE MOTH IMAGES













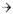 LOOKS LIKE LOOKS LIKE
|

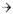 OTHER LIGHTBROWN APPLE MOTH IMAGES
OTHER LIGHTBROWN APPLE MOTH IMAGES











